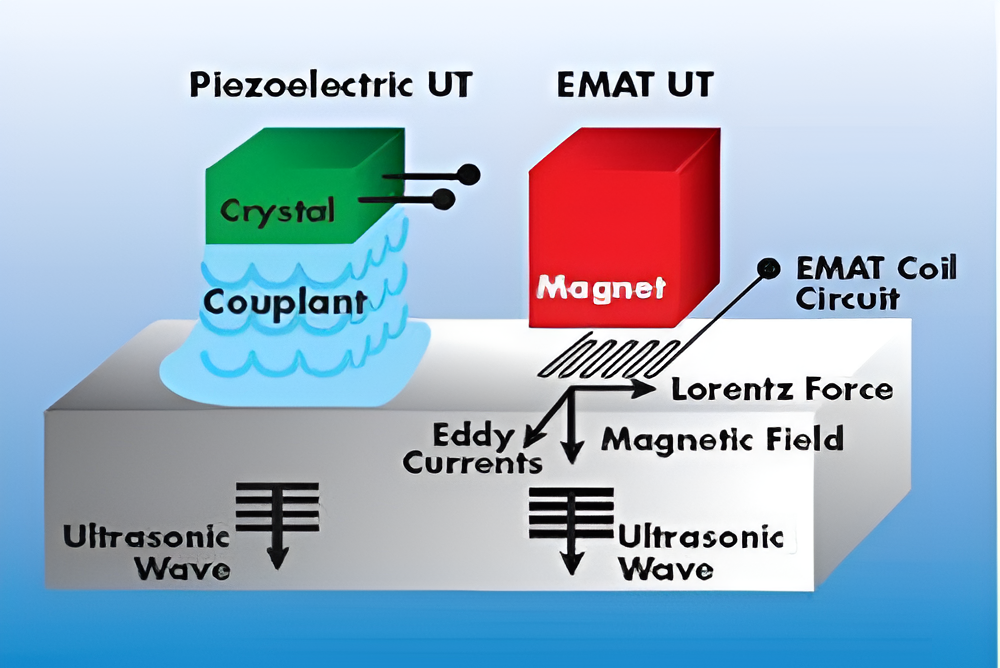
EMAT or Electro Magnetic Acoustic Transducer is an Ultrasonic Testing (UT) technique that generates the sound in the part inspected instead of the transducer. An EMAT induces ultrasonic waves into a test object with two interacting magnetic fields. A relatively high frequency (RF) field generated by electrical coils interacts with a low frequency or static field generated by magnets to generate a Lorentz force in a manner similar to an electric motor. This disturbance is transferred to the lattice of the material, producing an elastic wave. In a reciprocal process, the interaction of elastic waves in the presence of a magnetic field induces currents in the receiving EMAT coil circuit. For ferromagnetic conductors, produces additional stresses that enhance the signals to much higher levels than could be obtained by the Lorentz force alone. Various types of waves can be generated using different combinations of RF coils and magnets. EMATs have the following advantages over more conventional piezoelectric transducers:
Company
(+20) 1067260212
(+20) 01006126531
info@intergy.org
location
8B, Sakalya Street
Nasr City, Cairo , Egypt
©intergy, All rights reserved, Product by wpaper agency PureSoft